上篇文章 「Address Sanitizer 基本原理介绍及案例分析 」里我们简单地介绍了一下 Address Sanitizer 基础的工作原理,这里我们再继续深挖一下深层次的原理。
从上篇文章中我们也了解到,对一个内存地址的读 写
1 2 *address = ...; ... = *address;
当开启 Address Sanitizer 之后, 运行时库将会替换掉 malloc 和 free 函数,在 malloc 分配的内存区域前后设置 “投毒”(poisoned) 区域,使用 free 释放之后的内存也会被隔离并投毒,poisoned 区域也被称为 redzone。
上面的内存地址访问的代码,编译器会帮我们修改为这样的代码:
1 2 3 4 if (IsPoisoned (address)) { ReportError (address, kAccessSize, kIsWrite); } *address = ...;
这样对内存的访问,编译器会在编译期自动在所有内存访问之前通过判断 IsPoisoned(address) 做一下 check 是否被 “投毒”。
那么实现且高效地实现 IsPoisoned (),并使得 ReportError () 函数比较紧凑就十分重要。
在深入了解之前,我们先了解 Shadow 内存 ,以及主应用内存区 和 shadow 内存 映射。
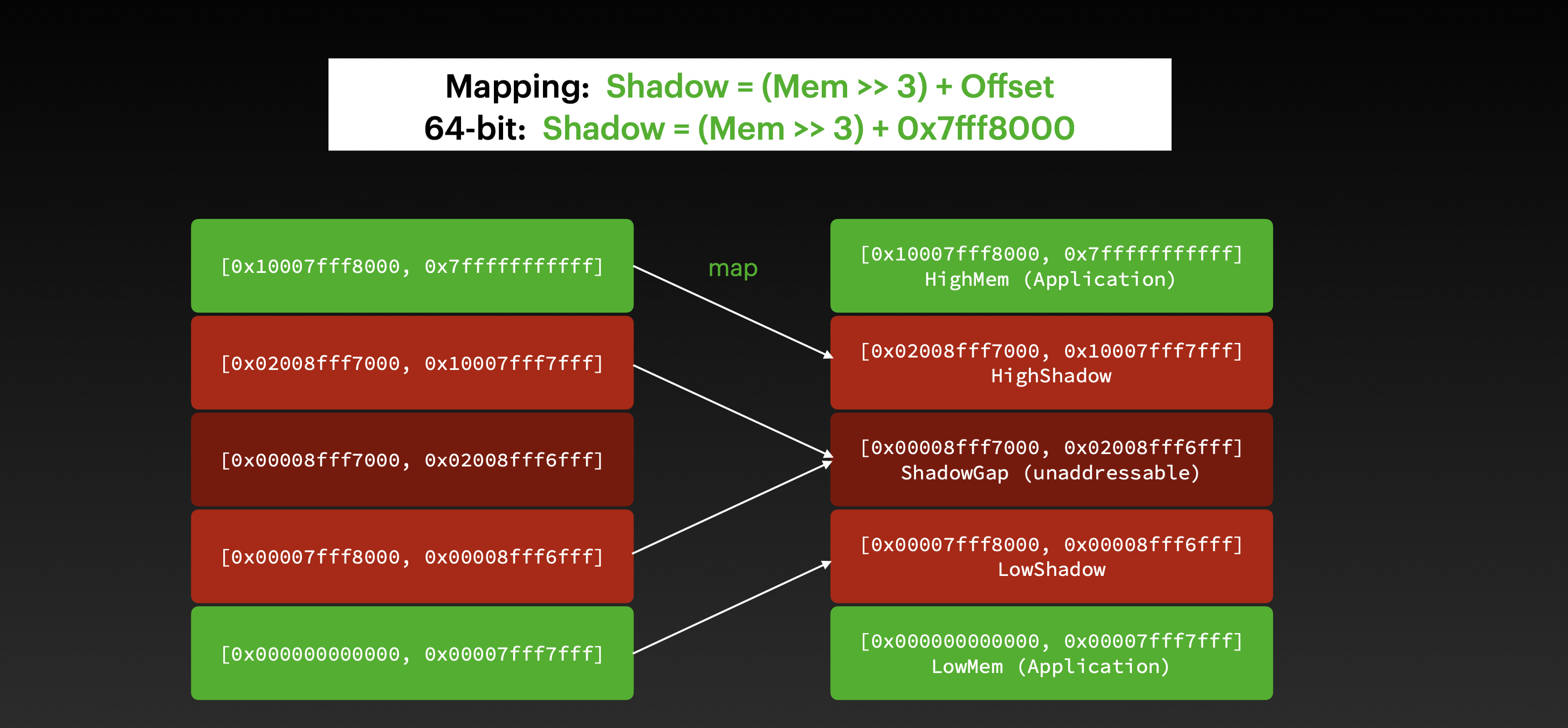
Shadow 内存 & 主应用内存区 和 shadow 内存 间的映射首先,虚拟内存地址被分配了两段不连续的区域:主应用内存区 和 shadow 内存区域。
更细一点来说,内存地址会分配 5 部分,最上和最下 (HighMem & LowMem) 都是应用内存区,他们会映射到 HighShadow 和 LowShadow 上,HighShadow 和 LowShadow 之间是 ShadowGap 区域,ShadowGap 区域是不可访问的,如果访问到会直接 crash.
为了节省内存占用,AddressSanitizer 会把 8 bytes 的应用内存会映射到 1 byte 的 shadow 内存。
从应用内存地址到 Shadow 内存地址映射算法是这样的:
1 Shadow = (Mem >>3 ) + Offset
查看 LLVM 的源码可以发现 offset 值因平台而异,这里就以 0x7fff8000 (1 << 46) 为例。
1 Shadow = (Mem >> 3 ) + 0x7fff8000 ;
映射图如下:
Shadow 内存的 9 种状态 这 1byte 的 shadown 内存会有 9 种值对应应用内存的状态:
负值,当 8 字节的应用内存全都被 poisoned 时;0 值,当且仅当 8 字节的应用内存都没有被 poisoned 时;1-7 值,为 k 的意思为 “前 k 个字节都没有被 poisoned,后 8-k 个字节被 poisoned”,这个是由 malloc 分配的内存总是 8 字节对齐作为前提来作为保证的。这样的话,当 malloc(13) 时,得到的是前一个 完整的 qword(8 字节,未被 poisoned)加上后一个 qword 的前 5 个 byte(未被 poisoned)
如何检查是否在 “投毒区”(poisoned/redzone)? 这样的话,我们就可以根据 shadow 内存的 9 种值来判断 引用内存的状态 了。
1 2 3 if (IsPoisoned (address)) { ReportError (address, kAccessSize, kIsWrite); }
扩展为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 byte *shadow_address = MemToShadow (address); byte shadow_value = *shadow_address; if (shadow_value) { if (SlowPathCheck (shadow_value, address, kAccessSize)) { ReportError (address, kAccessSize, kIsWrite); } } bool SlowPathCheck (shadow_value, address, kAccessSize) last_accessed_byte = (address & 7 ) + kAccessSize - 1 ; return (last_accessed_byte >= shadow_value); }
SlowPathCheck () 里,检查是否当前访问的地址的前若干个字节是否被 poisoned 了,因为是 8bytes 的应用内存映射到 1byte 的 shadow 上,首先要知道偏移,偏移 + 长度就是最后一个字节的位置,shadow_value <= 这个位置 - 1,说明被投毒了。
来看个例子。
比如应用内存 0x1000 - 0x1007 对应 shadow 的 0xF000 的地址
1 0x1000, 0x1001, 0x1002, 0x1003, 0x1004, 0x1005, 0x1006, 0x1007,
如果 0xF000 的值为 2, 就说明 0x1000, 0x1001 未被 poisoned,0x1002 到 0x1007 是被 poisoned 的。
那么,如果有一个 int 值在 0x1002 上,长度是 4 字节,那么我就需要检查 0x1005 以及之前(也就是前 6 个字节)是否被投毒,也就是检查 shadow value 是否 <= 5,如果小于等于 5,就说明只有前 5 个或者更少未被 poisoned,第 6 个字节一定被 poisoned 了,也就是这个 int 值肯定是被 poisoned 了。
再来看计算公式:
LLVM 里的实现源码 实际上,LLVM 是通过自定义 LLVM Pass 来插入指令并配合运行时库来完成上面的操作的。AddressSanitizer.cpp
源码超级长,我们只挑和上面相关的,首先定义了 static const uint64_t kDefaultShadowScale = 3;
AddressSanitizerLegacyPass 继承自 FunctionPass,override 了 runOnFunction(Function &F),也就可以对所有的函数进行修改和操作。runOnFunction 实现内部,创建了 AddressSanitizer 的实例,并调用了其 instrumentFunction(F, TLI) 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class AddressSanitizerLegacyPass : public FunctionPass {public : static char ID; explicit AddressSanitizerLegacyPass ( bool CompileKernel = false , bool Recover = false , bool UseAfterScope = false , AsanDetectStackUseAfterReturnMode UseAfterReturn = AsanDetectStackUseAfterReturnMode::Runtime) : FunctionPass(ID), CompileKernel(CompileKernel), Recover(Recover), UseAfterScope(UseAfterScope), UseAfterReturn(UseAfterReturn) { initializeAddressSanitizerLegacyPassPass (*PassRegistry::getPassRegistry ()); } bool runOnFunction (Function &F) override GlobalsMetadata &GlobalsMD = getAnalysis <ASanGlobalsMetadataWrapperPass>().getGlobalsMD (); const StackSafetyGlobalInfo *const SSGI = ClUseStackSafety ? &getAnalysis <StackSafetyGlobalInfoWrapperPass>().getResult () : nullptr ; const TargetLibraryInfo *TLI = &getAnalysis <TargetLibraryInfoWrapperPass>().getTLI (F); AddressSanitizer ASan (*F.getParent(), &GlobalsMD, SSGI, CompileKernel, Recover, UseAfterScope, UseAfterReturn) return ASan.instrumentFunction (F, TLI); }
AddressSanitizer::instrumentFunction 内容很长,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 bool AddressSanitizer::instrumentFunction (Function &F, const TargetLibraryInfo *TLI) ... SmallPtrSet<Value *, 16 > TempsToInstrument; SmallVector<InterestingMemoryOperand, 16 > OperandsToInstrument; SmallVector<MemIntrinsic *, 16 > IntrinToInstrument; SmallVector<Instruction *, 8 > NoReturnCalls; SmallVector<BasicBlock *, 16 > AllBlocks; SmallVector<Instruction *, 16 > PointerComparisonsOrSubtracts; for (auto &BB : F) { AllBlocks.push_back (&BB); TempsToInstrument.clear (); int NumInsnsPerBB = 0 ; for (auto &Inst : BB) { if (LooksLikeCodeInBug11395 (&Inst)) return false ; SmallVector<InterestingMemoryOperand, 1 > InterestingOperands; 🌟🌟🌟 getInterestingMemoryOperands (&Inst, InterestingOperands); if (!InterestingOperands.empty ()) { for (auto &Operand : InterestingOperands) { ... OperandsToInstrument.push_back (Operand); NumInsnsPerBB++; } } ... } } ... int NumInstrumented = 0 ; for (auto &Operand : OperandsToInstrument) { if (!suppressInstrumentationSiteForDebug (NumInstrumented)) 🌟🌟🌟 instrumentMop (ObjSizeVis, Operand, UseCalls, F.getParent ()->getDataLayout ()); FunctionModified = true ; } ... LLVM_DEBUG (dbgs () << "ASAN done instrumenting: " << FunctionModified << " " << F << "\n" ); return FunctionModified; }
AddressSanitizer::getInterestingMemoryOperands() 判断传入的指令 I 是否为感兴趣的 load 和 store 指令,把指令和地址信息放入 Interesting vector 里。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void AddressSanitizer::getInterestingMemoryOperands ( Instruction *I, SmallVectorImpl<InterestingMemoryOperand> &Interesting) if (LoadInst *LI = dyn_cast <LoadInst>(I)) { if (!ClInstrumentReads || ignoreAccess (I, LI->getPointerOperand ())) return ; Interesting.emplace_back (I, LI->getPointerOperandIndex (), false , LI->getType (), LI->getAlign ()); } else if (StoreInst *SI = dyn_cast <StoreInst>(I)) { if (!ClInstrumentWrites || ignoreAccess (I, SI->getPointerOperand ())) return ; Interesting.emplace_back (I, SI->getPointerOperandIndex (), true , SI->getValueOperand ()->getType (), SI->getAlign ()); } else if (AtomicRMWInst *RMW = dyn_cast <AtomicRMWInst>(I)) { ....
AddressSanitizer::instrumentMop()
Calls
void doInstrumentAddress()
Calls
AddressSanitizer::instrumentAddress() 是插入前面提到的内存判断的地方,函数比较长,这里省略掉不太影响理解的代码。InsertBefore 指令就是前面找到的 load/store 指令。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 void AddressSanitizer::instrumentAddress (Instruction *OrigIns, Instruction *InsertBefore, Value *Addr, uint32_t TypeSize, bool IsWrite, Value *SizeArgument, bool UseCalls, uint32_t Exp) Value *AddrLong = IRB.CreatePointerCast (Addr, IntptrTy); Type *ShadowTy = IntegerType::get (*C, std::max (8U , TypeSize >> Mapping.Scale)); Type *ShadowPtrTy = PointerType::get (ShadowTy, 0 ); Value *ShadowPtr = memToShadow (AddrLong, IRB); Value *CmpVal = Constant::getNullValue (ShadowTy); Value *ShadowValue = IRB.CreateLoad (ShadowTy, IRB.CreateIntToPtr (ShadowPtr, ShadowPtrTy)); Value *Cmp = IRB.CreateICmpNE (ShadowValue, CmpVal); size_t Granularity = 1ULL << Mapping.Scale; Instruction *CrashTerm = nullptr ; if (ClAlwaysSlowPath || (TypeSize < 8 * Granularity)) { Instruction *CheckTerm = SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen ( Cmp, InsertBefore, false , MDBuilder (*C).createBranchWeights (1 , 100000 )); assert (cast <BranchInst>(CheckTerm)->isUnconditional ()); BasicBlock *NextBB = CheckTerm->getSuccessor (0 ); IRB.SetInsertPoint (CheckTerm); Value *Cmp2 = createSlowPathCmp (IRB, AddrLong, ShadowValue, TypeSize); if (Recover) { CrashTerm = SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen (Cmp2, CheckTerm, false ); } else { BasicBlock *CrashBlock = BasicBlock::Create (*C, "" , NextBB->getParent (), NextBB); CrashTerm = new UnreachableInst (*C, CrashBlock); BranchInst *NewTerm = BranchInst::Create (CrashBlock, NextBB, Cmp2); ReplaceInstWithInst (CheckTerm, NewTerm); } } else { CrashTerm = SplitBlockAndInsertIfThen (Cmp, InsertBefore, !Recover); } Instruction *Crash = generateCrashCode (CrashTerm, AddrLong, IsWrite, AccessSizeIndex, SizeArgument, Exp); Crash->setDebugLoc (OrigIns->getDebugLoc ()); }
看一下 AddressSanitizer::memToShadow() 的实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Value *AddressSanitizer::memToShadow (Value *Shadow, IRBuilder<> &IRB) { Shadow = IRB.CreateLShr (Shadow, Mapping.Scale); if (Mapping.Offset == 0 ) return Shadow; Value *ShadowBase; if (LocalDynamicShadow) ShadowBase = LocalDynamicShadow; else ShadowBase = ConstantInt::get (IntptrTy, Mapping.Offset); if (Mapping.OrShadowOffset) return IRB.CreateOr (Shadow, ShadowBase); else return IRB.CreateAdd (Shadow, ShadowBase); }
Value *AddressSanitizer::createSlowPathCmp()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Value *AddressSanitizer::createSlowPathCmp (IRBuilder<> &IRB, Value *AddrLong, Value *ShadowValue, uint32_t TypeSize) size_t Granularity = static_cast <size_t >(1 ) << Mapping.Scale; Value *LastAccessedByte = IRB.CreateAnd (AddrLong, ConstantInt::get (IntptrTy, Granularity - 1 )); if (TypeSize / 8 > 1 ) LastAccessedByte = IRB.CreateAdd ( LastAccessedByte, ConstantInt::get (IntptrTy, TypeSize / 8 - 1 )); LastAccessedByte = IRB.CreateIntCast (LastAccessedByte, ShadowValue->getType (), false ); return IRB.CreateICmpSGE (LastAccessedByte, ShadowValue); }
Ref & 扩展阅读
AddressSanitizerAlgorithm Finding races and memory errors with LLVM instrumentation - Konstantin Serebryany, Google on 2011 LLVM Developers’ MeetingLLVM AddressSanitizer source code